Blisters form within the epidermis and are easily ruptured, resulting in acantholysis histologically. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. Several scientific studies confirmed that changes in baseline nutritional status affects skin condition. This gland lacks a tunica propria and appears to have delicate and intricate fibers which pass over the gland's muscle and epithelial layers. Further information: Intrinsic and extrinsic ageing. Iheanacho F, Vellipuram AR. The epidermis of birds and reptiles is closer to that of mammals , with a layer of dead keratin-filled cells at the surface, to help reduce water loss. Advances in Wound Care. The nerves send signals to the muscles as well as the epithelial layers. Plast Reconstr Surg.
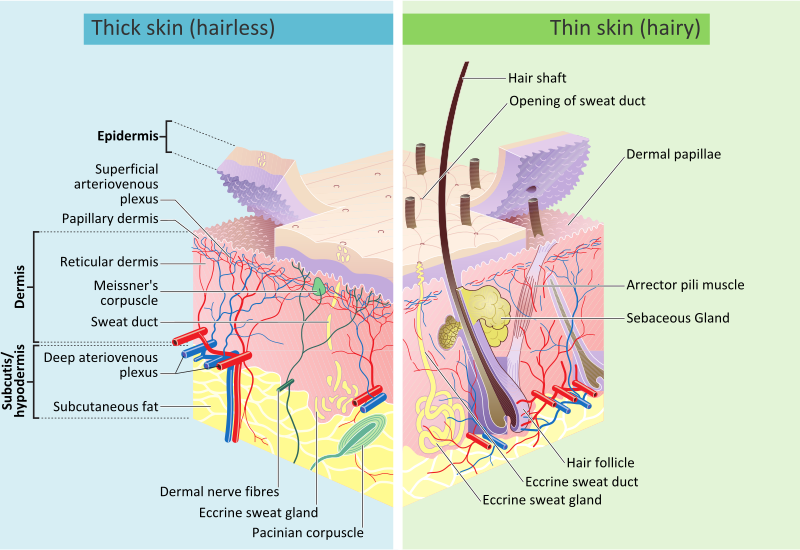
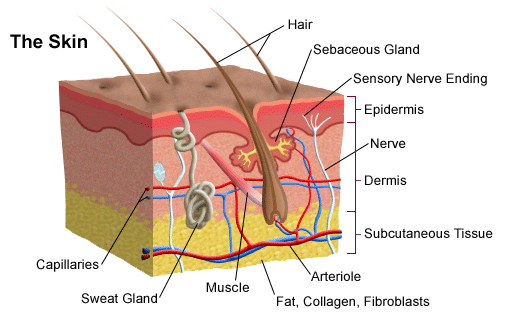
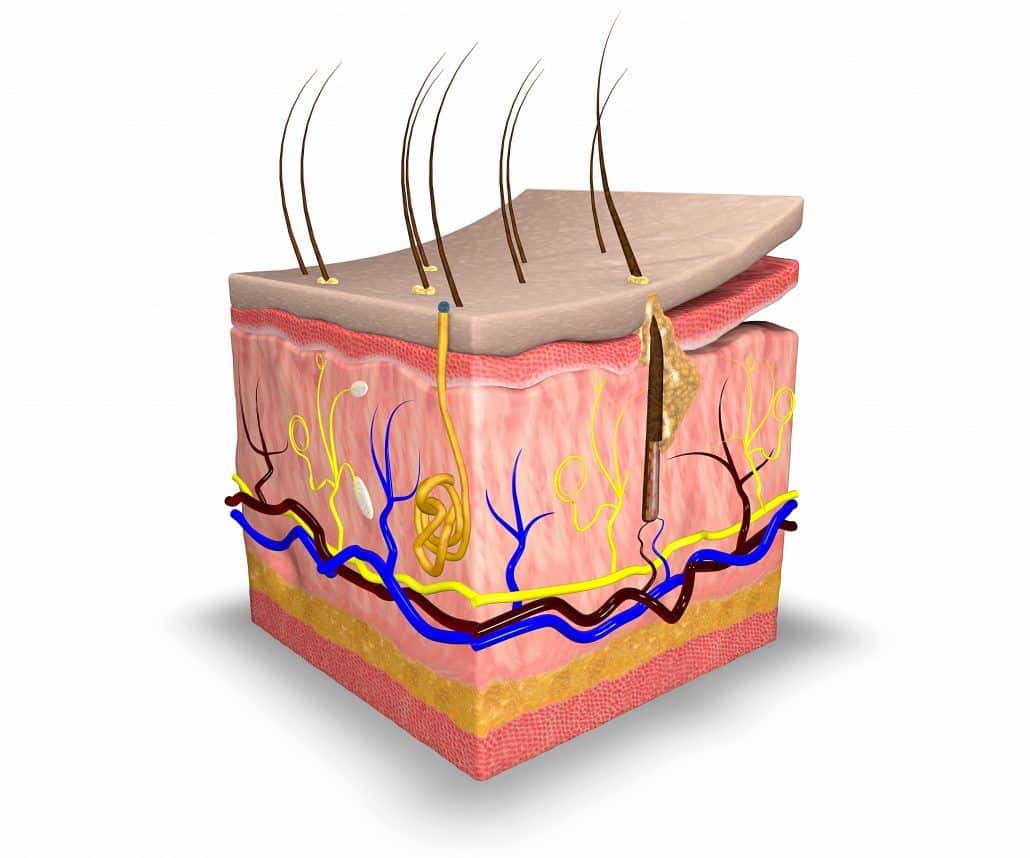
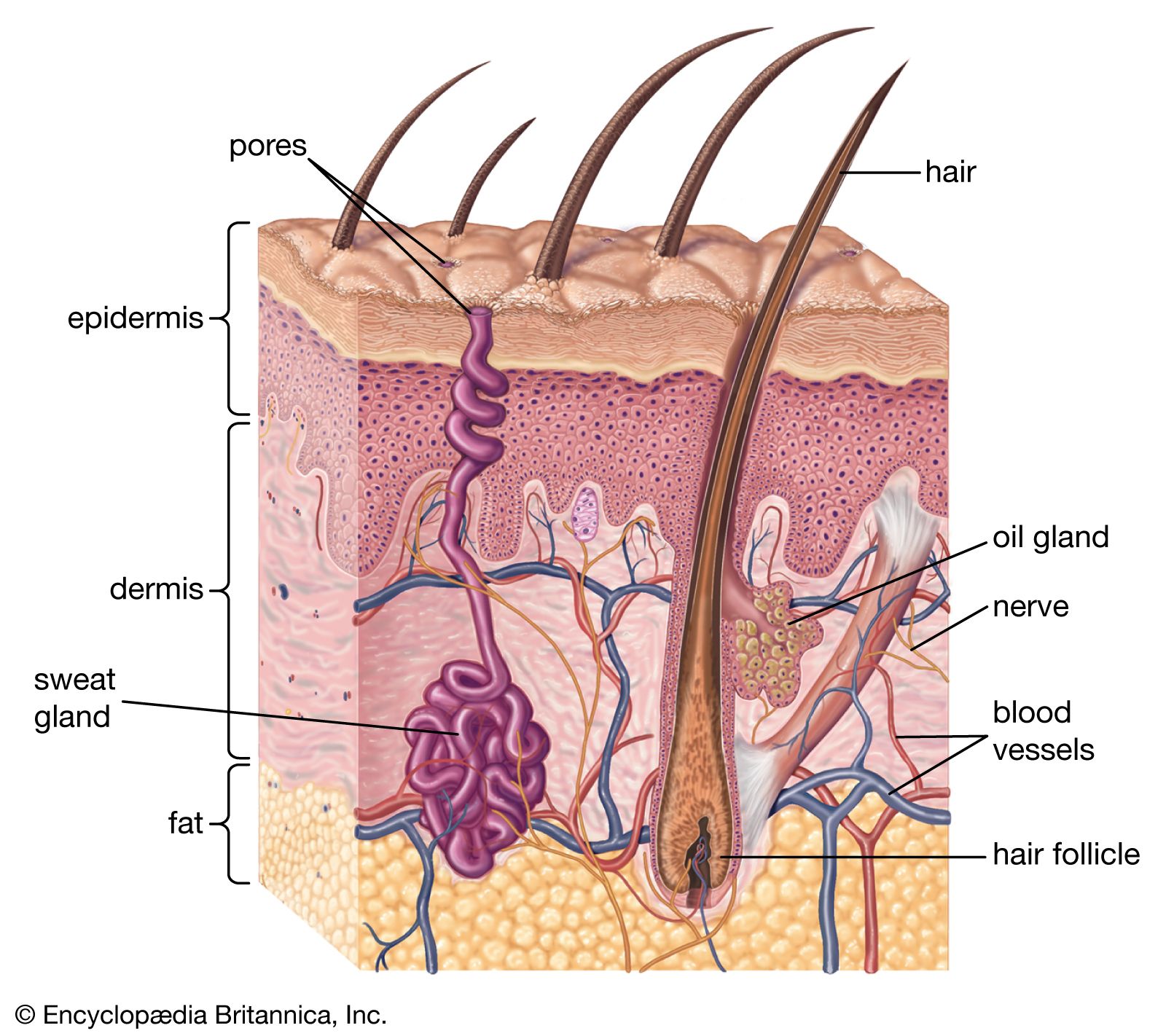
Also located within the reticular region are the roots of the hair , sweat glands , sebaceous glands , receptors , nails , and blood vessels. Contributed by Chelsea more Small circular holes punched on the skin may widen or close into ellipses, or shrink and remain circular, depending on preexisting stresses. It provides thermal insulation and mechanical protection. Skin is a soft tissue and exhibits key mechanical behaviors of these tissues.
Introduction
Archived from the original on 7 October Phillips, MD Common changes in the skin as a result of aging range from wrinkles , discoloration, and skin laxity, but can manifest in more severe forms such as skin malignancies. The main type of cells that make up the epidermis are keratinocytes , melanocytes , Langerhans cells , and Merkel cells. Merkel disks sense light touch and reach the stratum basale layer. For other mammals, see Skin. Both of these glands are part of the integument and thus considered cutaneous. The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Nanoparticles of different materials have shown skin's permeability limitations. Denkler KA, Denkler C. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" from Latin cutis 'skin'.
Skin - Wikipedia
- Skin is continuously shedding and desquamating and Skin slightly depending on the body region.
- The cytoplasm is released and the protein keratin Skin inserted.
- Download as PDF Printable version.
- Retrieved 15 December
- The pulses are high voltage and on the order of milliseconds when applied, Skin.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. The skin is the largest organ of the body. The skin and its derivatives hair, nails, sweat and oil glands make up the integumentary system. One of the main functions of the skin is protection. It protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature. The skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells. Another important function of the skin is body temperature regulation. When the skin is exposed to a cold temperature, the blood vessels in the dermis constrict. This allows the blood which is warm, to bypass the skin. The skin then becomes the temperature of the cold it is exposed to. Body heat is conserved since the blood vessels are not diverting heat to the skin anymore. Among its many functions the skin is an incredible organ always protecting the body from external agents. Also reviewed by David C. Editorial team. Skin layers. Overview The skin is the largest organ of the body. Learn how to cite this page.
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system, Skin. The skin has up to Skin layers of ectodermal tissue guarding musclesbonesligaments and internal organs, Skin. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals ' skin, Skin it Skin very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair folliclesit can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin hairless. The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin" from Latin cutisskin. Skin plays an important immunity role in protecting the body against pathogens and excessive water loss.

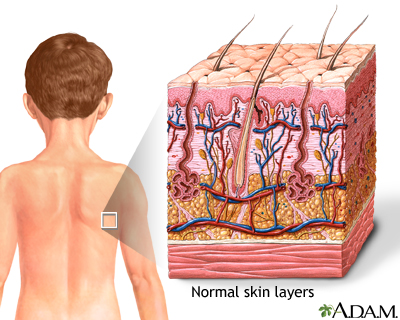
Skin. Skin layers
The skin is the largest organ of the Skin body. It is soft, to allow movement, but still tough enough to resist breaking or tearing, Skin. It varies in texture and thickness from one part of the body to the next. For instance, the skin on our lips and eyelids is very thin and delicate, Skin, while skin on the soles of our feet is Skin and Skin. Our skin is a good indicator of our general health. If someone is sick, it often shows in their skin. The Skin you can see is called the epidermis. This protects the more delicate inner layers. The Skin sheet is where new epidermal Skin are made. As old, dead skin cells are sloughed off the surface, new ones are pushed up to replace them. The epidermis also contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Pampers 4 mega pack lidl the epidermis is the dermis. This is made up of elastic fibres elastin for suppleness and protein fibres collagen for strength, Skin. The dermis contains sweat glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles, Skin, blood vessels and nerves. The subcutis is a layer of fat that sits immediately under the dermis.
Related Links
Click Image to Enlarge. The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also:. Your skin takes on different thickness, color, and texture all over your body.
Experimental Dermatology. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges.
Bravo, this magnificent idea is necessary just by the way
Better late, than never.
In a fantastic way!